Last modified August 11, 2024
Anti-spam and anti-virus fight
This site has been automatically translated with Google Translate from this original page written in french, there may be some translation errors
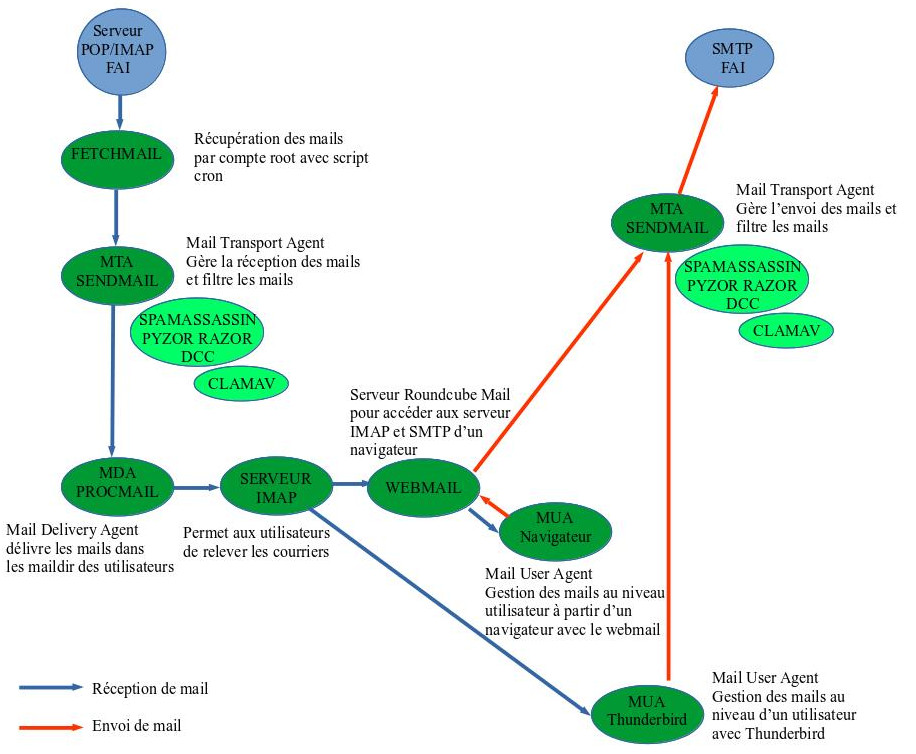
Configuration Overview
- procmail allows you to filter with static rules emails that have already been delivered by the local mail server (MTA)
The most sophisticated tools are
- SpamAssassin for the fight against spam which uses for better efficiency three other tools of the same kind namely Razor, Pyzor and DCC
- clam anti virus for the fight against viruses.
Basic filtering with procmail
:0
*
^Subject:.*ILOVEYOU
/dev/null
You just have to adapt this rule according to the subject (or from). This other very useful rule allows you to save in a virus file all the emails arriving with the extensions mentioned there.
:0 H
*^Content-type:
(multipart/mixed)
{
:0 B
*^Content-Disposition:
(attachment|inline)
*filename=".*\.(ocx|vbs|wsf|shs|exe|com|bat|chm|pif|vbe|hta|scr)"
{
:0
virus
}
}
The virus file can be opened as a mailbox with software like kmail. The following filter
:0^Subject:.*[^ -~][^ -~][^ -~][^ -~]
/dev/null
Filter spam with SpamAssassin
Presentation
SpamAssassin is an anti-spam software, it is based among other things on heuristic and Bayesian analysis of emails and uses other anti-spam techniques and tools such as pyzor, razor and DCC which are presented below
Filtering techniques
Heuristic filtering
It is a technique that allows spam to be identified based on certain common characteristics (punctuation, html, link to an image, etc.)Bayesian filtering
Bayesian filtering is based on the principle that an event can occur based on the same events that occurred previously. In short, for email, if we encounter certain words or phrases more often in emails classified as spam than in emails classified as normal, we can assume that the next time we encounter these same words and phrases, there is a good chance that it will be in a spam email.
For this, a database of words and phrases is created and enriched as emails are received and sent that are valid or considered spam. Each word or sentence receives a value calculated according to the probability that it is linked to spam, it depends on the number of times the term appears in spam compared to the number of times the same term is encountered in valid mail. Consequently, some words may have a high probability of being linked to spam for some users and not for others, concrete example a company working in the medical field the term "drug" will have a low probability of being linked to spam because it is very often used in valid emails, for other people this term will be systematically linked to spam. Consequently the Bayesian filter has the particularity and advantage of adapting to the user, it reduces the risk of false positives (valid mail considered spam). Furthermore, the filter is not static, the database is constantly evolving and therefore the filter will become more and more efficient day by day and will adapt according to the users of your network and the new techniques used by spammers.
Concrete example of the last point, until now spammers sent emails with words like "sex, free, viagra, ...", it was quite simple to set up a filter based on keywords to delete the emails in question, spammers have therefore slightly modified the semantics of words "sex, fre e" or even "v$i$a$g$r$a", with a simple filtering by keywords, it is almost impossible to establish an effective rule to filter these emails. The Bayesian filter will have no problem assigning it a high spam probability value.
Another advantage of the Bayesian filter, and not the least, is that it adapts to all languages.
In short, for a spammer to be able to fool a Bayesian filter, he must know the user he wants to reach and avoid using the words that the user in question uses the least...
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
s=leboncoin; t=1723375141;
bh=HAcQhfWcguB9ox41T/Matzz+tV45lns6A9KqbTYQ/78=;
h=From:Subject:Date:To:MIME-Version:Message-ID:
List-Unsubscribe-Post:List-Unsubscribe:Content-Type;
b=pCqi9SNfg44gmKtLWTsgRQjnNm6oeWbiNzvFG0YhKoh/FvnnZwfBGl6hOCWxjUj4L
67ejz/r3S1wHEeD5Z0VrQMPlEqPlc8b/yFZv4jX+7pUrWIeLUcZ1jDQABfRY3Kjgh1
i/fvJHmYdjjGqoaXsu24hOsCWiR/35oYsRVpQDKF8nCAj05bRNB0VKyXzyZnf4gBKt
lWGbiT4gNviIsBwloFY9Z6HZcZRbGfG+LnAbUYOEOyDSFOQMcc0AbMHRLH7z8gk10u
PLdWf8JTakjCQVbQP0EmQekZwcprdeU3tukyisKGVrsuYeNtSFqUSibxJIT6PzIjia
w/XAbguDMdq2A==
SPF is a sender authentication technique to prevent
domain spoofing. It checks whether the domain name is
authorized to send an email and checks whether its IP
address is correct.
Facility
Razor Installation
Now we will retrieve razor which will complete SpamAssassin in the spam search on this URL https://sourceforge.net/projects/razor/files/razor-agents/ . We unzip the archive by typing
tar xvfz razor-agents-2.85.tar.gz
This gives the directory razor-agents-2.85 , before going further it will be necessary to install as root the following perl modules
perl -MCPAN -e shell
Then at the prompt
install Digest::SHA1
install Digest::HMAC_MD5
In the razor-agents-2.85 directory we now type
perl Makefile.PL
Then we edit the Makefile to put the correct installation path
INSTALL_BASE = /usr/local
et on tape make puis en tant que root
make install
Here is the trace of razor2 by typing journalctl with SpamAssassin debug mode
Aug 10 17:47:18 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: razor2: part=0 engine=8 contested=0 confidence=0
Aug 10 17:47:18 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: razor2: part=1 engine=8 contested=0 confidence=0
Aug 10 17:47:18 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: razor2: results: spam? 0
(...)
in case of positive response for spam
Aug 11 12:21:53
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: razor2: child process 422176
finished, reading results
Aug 11 12:21:53
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: razor2: part=0 engine=8
contested=0 confidence=100
Aug 11 12:21:53
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: razor2: results: spam? 1
Aug 11 12:21:53
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: razor2: results: engine 8,
highest cf score: 100
I deduce that razor2 works correctly, on the other hand if we have this error
Sep 29 17:10:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[657127]: razor2: razor2 check failed: Connection reset by peer razor2: razor2 had unknown error during check at /usr/local/share/perl5/5.36/Mail/SpamAssassin/Plugin/Razor2.pm line 230, <GEN60> line 1. at /usr/local/share/perl5/5.36/Mail/SpamAssassin/Plugin/Razor2.pm line 350.
we will create the following directory
mkdir /etc/mail/spamassassin/razor
then we will type the following command
razor-admin -home=/etc/mail/spamassassin/razor -register
here is the result
Register successful. Identity stored in /etc/mail/spamassassin/razor/identity-ruX-WiLff-
then we type
razor-admin
-home=/etc/mail/spamassassin/razor -create
razor-admin -home=/etc/mail/spamassassin/razor -discover
under the directory /etc/mail/spamassassin/razor we will find these files
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 19
Sep 29 17:19 identity -> identity-ruX-WiLff-
-rw------- 1 root root 90
Sep 29 17:19 identity-ruX-WiLff-
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 706
Sep 29 17:20 razor-agent.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root
1018 Sep 29 17:20 razor-agent.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 785
Sep 29 17:19 server.n002.cloudmark.com.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 57
Sep 29 17:20 servers.catalogue.lst
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root Sep
30, 29 5:20 p.m. servers.discovery.lst
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root Sep
76, 29 5:20 p.m. servers.nomination.lst
Installing SpamAssassin
SpamAssassin will be retrieved from the site www.spamassassin.org/ . Unzip the archive by typingtar xvfz Mail-SpamAssassin-4.0.1.tar.gz
This gives the directory Mail-SpamAssassin-4.0.1 . Before going further I had to install the
urpmi packages perl-devel perl-Net-DNS perl-NetAddr-IP perl-Archive-Tar perl-Mail-SPF perl-IP-Country perl-Net-Ident perl-IO-Socket-INET6 perl-Mail-DKIM perl-DBI perl-Encode-Detect perl-Geo-IP perl-Archive-Zip perl-Net-Patricia perl-IO-String perl-BSD-Resource re2c perl-Email-Address-XS perl-Net-LibIDN perl-DBD-SQLite perl-Devel-Cycle perl-Text-Diff perl-Moo perl-MooX-StrictConstructor perl-Email-MIME
to be able to benefit from the geolocation of IP addresses we will install MaxMind as explained here and then type the command (without being root)
perl -MCPAN -e shell
and in the shell
install Net::LibIDN2
install
MaxMind::DB::Reader
install
MaxMind::DB::Reader::XS
install
IP::Country::DB_File
install Mail::DMARC
install Mail::DMARC::PurePerl
This will create a number of directories under ~/perl5 of your user that will need to be made accessible to everyone by copying them under /usr/lib64/perl5
Now let's go back to the Mail-SpamAssassin-4.0.1 directory and type
perl Makefile.PL PREFIX=/usr/local SYSCONFDIR=/etc
This is the resultWhat email address or URL
should be used in the suspected-spam report
text for users who want
more information on your filter installation?
(In particular, ISPs
should change this to a local Postmaster contact)
default text: [the
administrator of that system] olivier
NOTE: settings for "make
test" are now controlled using "t/config.dist".
See this file if you wish
to customize what tests are run, and how.
checking module
dependencies and their versions...
checking binary
dependencies and their versions...
dependency check
complete...
Warning: prerequisite
Perl::Critic::Policy::Perlsecret 0 not found.
Warning: prerequisite
Perl::Critic::Policy::TestingAndDebugging::ProhibitNoStrict
0 not found.
Generating a Unix-style
Makefile
Writing Makefile for
Mail::SpamAssassin
Writing MYMETA.yml and
MYMETA.json
Makefile written by
ExtUtils::MakeMaker 7.64
INSTALLSITECONF = /etc/mail/spamassassin
make
Then as root
make install
DCC Installation
Concretely, upon receipt of an email , the DCC client assigns it a digital signature (checksum), retrieves from the server the number of times that this signature appears in the central server, if this number exceeds a certain configurable value (threshold) and the sender of the email in question is not in the whitelist (also configurable), the email is considered spam and treated as such.
We will further expand SpamAssassin with DCC that we will retrieve here http://www.rhyolite.com/anti-spam/dcc/ . We unzip the archive by typing
tar xvfz dcc.tar.Z
This gives the dcc-2.3.169 directory . Now think about installing the sendmail-devel package, we return to the DCC directory in which we successively type
./configure
make
Then as root
make install
Now if we type
cdcc 'info'
We obtain
# 08/10/24
08:43:18 CEST /var/dcc/map
# Re-resolve names after
09:15:17 Check RTTs after 08:58:17
# 1270.85 ms threshold,
1237.84 ms average 12 total, 11 working
IPv6 servers on version=3
dcc1.dcc-servers.net,-
RTT+1000 ms anon
# 72.18.213.52,-
x.dcc-servers ID 104
# 100% of 32 requests ok
438.56+1000 ms RTT 300 ms queue wait
# *137.208.8.63,- wuwien
ID 1290
# 100% of 32 requests ok
138.30+1000ms RTT 100 ms queue wait
# 193.30.34.11,-
www.nova53.net ID 1204
# 100% of 32 requests ok
170.85+1000 ms RTT 70 ms queue wait
dcc2.dcc-servers.net,-
RTT+1000 ms anon
# 194.119.212.6,- dcc1 ID
1182
# 100% of 32 requests ok
973.70+1000 ms RTT 100 ms queue wait
# 204.90.71.235,-
MGTINTERNET ID 1170
# 100% of 32 requests ok
195.75+1000 ms RTT 100 ms queue wait
dcc3.dcc-servers.net,-
RTT+1000 ms anon
# 72.18.213.53,-
x.dcc-servers ID 104
# 100% of 32 requests ok
440.12+1000 ms RTT 300 ms queue wait
# 208.88.55.138,- ID 1006
# 100% of 32 requests ok
1075.27+1000 ms RTT 500 ms queue wait
dcc4.dcc-servers.net,-
RTT+1000 ms anon
# 72.18.213.51
,
- 1480
# 88% of 32 requests ok
1540.71+1000 ms RTT 1200 ms queue wait
dcc5.dcc-servers.net,-
RTT+1000 ms anon
# 157.131.0.46,- sonic ID
1255
# 100% of 32 requests ok
257.89+1000 ms RTT 100 ms queue wait
# 193.30.34.14,-
www.nova53.net ID 1207
# 100% of 32 requests ok
232.64+1000 ms RTT 130 ms queue wait
@,- RTT-1000 ms 32768
secret114454481y1031
#
127.0.0.1,-
# not answering
################
# 08/10/24 08:43:18 CEST
greylist /var/dcc/map
# Re-resolve names after
10:43:17
# 1 total, 0 working
servers
# continue not asking
greylist server 32 seconds after 1 failures
@,- Greylist 32768
secret114454481y1031
#
*127.0.0.1,6276
# not answering
When upgrading from a previous version I got the following error
open(/var/dcc/map): Too many open files
open(/tmp/map1MdBL2): Too many open files
?
I had no choice but to delete /var/run/dcc and redo a make install .
Here is the DCC trace by typing journalctl in SpamAssassin debug mode
Aug 11
10:08:08 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[233885]: util: executable for
cdcc was found at /usr/local/bin/cdcc
Aug 11 10:08:08
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[233885]: dcc: dcc_pgm_path, found cdcc
in env.path: /usr/local/bin/cdcc
Aug 11 10:08:08
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[233885]: dcc: `/usr/local/bin/cdcc -qV
homedir libexecdir` reports '2.3.169 homedir=/var/dcc
libexecdir=/var/dcc/libexec'
Aug 11 10:08:08
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[233885]: dcc: use 'dcc_libexec
/var/dcc/libexec' from cdcc
Aug 11 10:08:08
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[233885]: dcc: use 'dcc_home /var/dcc'
from cdcc
Aug 11 10:08:08
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[233885]: dcc: dccifd is not available;
no r/w socket at /var/dcc/dccif
Aug 11
12:52:05 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: timing: total 7617
ms - read_scoreonly_config: 128 (1.7%), signal_user_changed:
2.0 (0.0%), parse: 6 (0.1%), extract_message_metadata: 49
(0.6%), tests_pri_-10000: 16 (0.2%), get_uri_detail_list: 29
(0.4%), tests_pri_-2000: 5 (0.1%), tests_pri_-1000: 2.8
(0.0%), tests_pri_-950: 1.48 (0.0%), tests_pri_-900: 1.72
(0.0%), tests_pri_-100: 4623 (60.7%), check_spf: 42 (0.6%),
poll_dns_idle: 52 (0.7%), check_dkim_signature: 36 (0.5%),
check_dcc: 4312 (56.6%), check_razor2: 1429 (18.8%),
check_pyzor: 66 (0.9%), tests_pri_-90: 35 (0.5%),
check_bayes: 31 (0.4%), b_tokenize: 14 (0.2%),
b_tok_get_all: 7 (0.1%), b_comp_prob: 5 (0.1%),
b_tok_touch_all: 0.57 (0.0%), b_finish: 2.4 (0.0%),
tests_pri_0: 210 (2.8%), tests_pri_10: 6 (0.1%),
tests_pri_500: 2.8 (0.0%), tests_pri_1000: 91 (1.2%),
total_awl: 88 (1.2%), check_awl: 35 (0.5%), update_awl: 0.36
(0.0%), learn: 851 (11.2%), b_learn: 832 (10.9%),
b_count_change: 23 (0.3%), rewrite_mail: 3.0 (0.0%),
copy_config: 59 (0.8%)
Installing pyzor
pyzor also interfaces with SpamAssassin, you can find it here https://github.com/SpamExperts/pyzor , the latest version is 1.0.0 which generated the following message in the SpamAssassin logs
pyzor: internal error, python traceback seen in response: Traceback (most recent call last):
I had to install the development version, you unzip the archive by typing
unzip pyzor-master.zipThis gives the pyzor-master directory in which we type
python setup.py build
it will probably be necessary to first install the python-setuptools
package We become root then we type
python setup.py install
here is the trace of pyzor by typing journalctl in debug mode of SpamAssassin
August 11
07:33:05 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[231738]: util: executable for
pyzor was found at /usr/local/bin/pyzor
August 11 07:33:05
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[231738]: pyzor: pyzor is available:
/usr/local/bin/pyzor
August 10
18:17:30 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: pyzor: child process
172014 finished, reading results
August 10 18:17:30
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: pyzor: got response:
public.pyzor.org:24441\t(200, 'OK')\t0\t0
Aug 10 18:17:30
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: pyzor: result: COUNT=0/5
WELCOMELIST=0/10/0.0
Aug 10 18:17:30
ultra.kervao.fr spamd[169810]: check: tagrun - tag PYZOR is
now ready, value: Reported 0 times, welcome listed 0 times.
Oct 10 08:16:09 mana.kervao.fr spamd[1672]: timing: total 6413 ms - read_scoreonly_config: 1.53 (0.0%), signal_user_changed: 2.2 (0.0%), parse: 1.96 (0.0%), extract_message_metadata: 55 (0.9%), get_uri_detail_list: 2.5 (0.0%), tests_pri_-1000: 50 (0.8%), tests_pri_-950: 2.00 (0.0%), tests_pri_-900: 2.1 (0.0%), tests_pri_-400: 19 (0.3%), check_bayes: 16 (0.3%), b_tokenize: 6 (0.1%), b_tok_get_all: 3.5 (0.1%), b_comp_prob: 3.8 (0.1%), b_tok_touch_all: 0.38 (0.0%), b_finish: 1.53 (0.0%), tests_pri_0: 6179 (96.4%), check_spf: 17 (0.3%), poll_dns_idle: 0.17 (0.0%), check_dkim_signature: 0.71 (0.0%), check_dkim_adsp: 30 (0.5%), check_dcc: 4302 (67.1%), check_pyzor: 170 (2.6%), check_razor2: 1599 (24.9%), tests_pri_500: 10 (0.2%), tests_pri_1000: 6 (0.1%), total_awl: 4.1 (0.1%), check_awl: 0.36 (0.0%), update_awl: 0.21 (0.0%), learn: 6 (0.1%), b_learn: 2.6 (0.0%), rewrite_mail: 1.73 (0.0%), get_report: 0.58 (0.0%), copy_config: 39 (0.6%)
SpamAssassin Configuration
# RelayCountry - add metadata for Bayes learning, marking the countries
# a message was relayed through
#
# Note: This requires the Geo::IP Perl module
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::RelayCountry
# URIDNSBL - look up URLs found in the message against several DNS
# blocklists.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URIDNSBL
# Hashcash - perform hashcash verification.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Hashcash
# SPF - perform SPF verification.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::SPF
Here is my v310.pre configuration file which can be found under /etc/mail/spamassassin
# DCC - perform DCC message checks.
#
# DCC is disabled here because it is not open source. See the DCC
# license for more details.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DCC
# Pyzor - perform Pyzor message checks.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Pyzor
# Razor2 - perform Razor2 message checks.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Razor2
# SpamCop - perform SpamCop message reporting
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::SpamCop
# AntiVirus - some simple anti-virus checks, this is not a replacement
# for an anti-virus filter like Clam AntiVirus
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AntiVirus
# AWL - do auto-whitelist checks
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AWL
# AutoLearnThreshold - threshold-based discriminator for Bayes auto-learning
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AutoLearnThreshold
# TextCat - language guesser
# we will activate this plugin to filter emails written in Chinese or Arabic or other
loadplugins Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::TextCat
# AccessDB - lookup from-addresses in access database
#
#loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AccessDB
# WhitelistSubject - Whitelist/Blacklist certain subject regular expressions
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::WhiteListSubject
#########################################################################
# experimental plugins
# DomainKeys - perform DomainKeys verification
#
# This plugin has been removed as of v3.3.0. Use the DKIM plugin instead,
# which supports both Domain Keys and DKIM.
# MIMEHeader - apply regexp rules against MIME headers in the message
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::MIMEHeader
# ReplaceTags
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ReplaceTags the
v312.pre file
###############################################
# experimental plugins
# DKIM - perform DKIM
verification
#
# Mail::DKIM module
required for use, see INSTALL for more information.
#
# Note that if
C<Mail::DKIM> version 0.20 or later is installed,
this
# renders the DomainKeys
plugin redundant.
#
loadplugin
Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DKIM
# Check - Provides main check functionality
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Check
# HTTPSMismatch - find URI mismatches between href and anchor text
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HTTPSMismatch
# URIDetail - test URIs using detailed URI information
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URIDetail
# Shortcircuit - stop evaluation early if high-accuracy rules fire
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Shortcircuit
# Plugins which used to be EvalTests.pm
# broken out into separate plugins
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Bayes
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::BodyEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DNSEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HTMLEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HeaderEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::MIMEEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::RelayEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URIEval
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::WLBLEval
# VBounce - anti-bounce-message rules, see rules/20_vbounce.cf
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::VBounce
# Rule2XSBody - speedup by compilation of ruleset to native code
#
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Rule2XSBody
# ASN - Look up the Autonomous System Number of the connecting IP
# and create a header containing ASN data for bayes tokenization.
# See plugin's POD docs for usage info.
#
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ASN
# ImageInfo - rules to match metadata of image attachments
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ImageInfo
v330.pre file
###################################################
# PhishTag - allows sites to rewrite suspect phish-mail URLs
# (Note: this requires configuration, see http://umut.topkara.org/PhishTag)
#
#loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::PhishTag
# FreeMail - detect email addresses using free webmail services,
# usable as input for other rules
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::FreeMail
v340.pre file# This is the right place to customize your installation of SpamAssassin.
#
# See 'perldoc Mail::SpamAssassin::Conf' for details of what can be
# tweaked.
#
# This file was installed during the installation of SpamAssassin 3.4.0,
# and contains plugin loading commands for the new plugins added in that
# release. It will not be overwritten during future SpamAssassin installs,
# so you can modify it to enable some disabled-by-default plugins below,
# if you so wish.
#
# There are now multiple files read to enable plugins in the
# /etc/mail/spamassassin directory; previously only one, "init.pre" was
# read. Now both "init.pre", "v310.pre", and any other files ending in
# ".pre" will be read. As future releases are made, new plugins will be
# added to new files, named according to the release they're added in.
###########################################################################
# AskDNS - forms a DNS query based on 'tags' as supplied by other plugins
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AskDNS
v341.pre file
# TxRep - Reputation database that replaces AWL
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::TxRep
# URILocalBL - Provides ISP and Country code based filtering as well as
# quick IP based blocks without a full RBL implementation - Bug 7060
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URILocalBL
# PDFInfo - Use several methods to detect a PDF file's ham/spam traits
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::PDFInfo
v342.pre file
# FromNameSpoof - help stop spam that tries to spoof
other domains using
# the from name
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::FromNameSpoof
# Phishing - finds uris used in phishing campaigns detected by
# OpenPhish or PhishTank feeds.
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Phishing
v343.pre file has no loadplugin enabled, content of v400pre
# ExtractText - Extract text from documents or
images for matching
#
# Requires manual configuration, see plugin documentation.
#
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ExtractText
# DecodeShortUrl - Check for shortened URLs
#
# Note that this plugin will send HTTP requests to different
URL shortener
# services. Enabling caching is recommended, see
plugin documentation.
#
# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DecodeShortURLs
# DMARC - Check DMARC compliance
#
# Requires Mail::DMARC module and working SPF and DKIM
Plugins.
#
loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DMARC
and here is my local.cf
file
allow_user_rules 1
# Add *****SPAM***** to the Subject header of spam
e-mails
#
rewrite_header Subject *****SPAM*****
# Save spam messages as a message/rfc822 MIME
attachment instead of
# modifying the original message (0: off, 2: use
text/plain instead)
#
report_safe 1
# rajout de cette option pour bien prendre en compte
# les accents dans le rapport spamassassin
report_charset iso-8859-1
# Set which networks or hosts are
considered 'trusted' by your mail
# server (i.e. not spammers)
#
# trusted_networks 212.17.35.
# Set file-locking method (flock is not safe over
NFS, but is faster)
#
# lock_method flock
# Set the threshold at which a message is
considered spam (default: 5.0)
#
required_score 5.0
score USER_IN_WELCOMELIST -100.0
score USER_IN_BLOCKLIST 100.0
use_auto_whitelist 1
#use_txrep 1
# pour filtrer les mails en chinois
# on autorise que ces langues, les autres sont
# considérés comme spam avec un score de 10
ok_languages en fr ca de es it pt
score UNWANTED_LANGUAGE_BODY 10
add_header all Languages _LANGUAGES_
# Use Bayesian classifier (default: 1)
#
use_bayes 1
use_bayes_rules 1
# Bayesian classifier auto-learning (default: 1)
#
bayes_auto_learn 1
#bayes_auto_learn_threshold_nonspam -2.0
bayes_auto_learn_threshold_spam 6.0
header
AWL
eval:check_from_in_auto_whitelist()
describe
AWL
From: address is in the auto white-list
tflags
AWL
userconf noautolearn
priority
AWL
1000
#header
TXREP eval:check_senders_reputation()
#describe
TXREP Score normalizing based on sender's
reputation
#tflags
TXREP userconf noautolearn
#priority
TXREP 1000
#tflags URIBL_DBL_SPAM autolearn_force
#tflags URIBL_JP_SURBL autolearn_force
#tflags URIBL_BLACK autolearn_force
#tflags INVALID_DATE autolearn_force
# Set headers which may provide inappropriate cues
to the Bayesian
# classifier
#
# bayes_ignore_header X-Bogosity
# bayes_ignore_header X-Spam-Flag
# bayes_ignore_header X-Spam-Status
bayes_path /var/spool/mail/.spamassassin/bayes
bayes_file_mode 0777
# Whether to decode non- UTF-8 and non-ASCII
textual parts and recodeA
#
# them to UTF-8 before the text is given over to
rules processing.
#
# normalize_charset 1
# Some shortcircuiting, if the plugin is enabled
#
ifplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Shortcircuit
#
# default: strongly-whitelisted mails are *really*
whitelisted now, if the
# shortcircuiting plugin is active, causing early
exit to save CPU load.
# Uncomment to turn this on
#
shortcircuit
USER_IN_WELCOMELIST on
# shortcircuit USER_IN_DEF_WHITELIST on
# shortcircuit USER_IN_ALL_SPAM_TO on
# shortcircuit SUBJECT_IN_WHITELIST on
# the opposite; blacklisted mails can also save
CPU
#
shortcircuit
USER_IN_BLOCKLIST on
# shortcircuit USER_IN_BLACKLIST_TO on
# shortcircuit SUBJECT_IN_BLACKLIST on
# if you have taken the time to correctly specify
your "trusted_networks",
# this is another good way to save CPU
#
# shortcircuit
ALL_TRUSTED
on
# and a well-trained bayes DB can save running
rules, too
#
# shortcircuit
BAYES_99
spam
# shortcircuit
BAYES_00
ham
#endif
I had a problem when I was retrieving my users' emails, the mail user could not create a file in their homedirectory
Oct 2 09:58:53 tosh spamd[1676]: debug: open of AWL file failed: lock: 1676 cannot create tmp lockfile /home/olivier/.spamassassin/auto-whitelist.lock.tosh.kervao.fr.1676 for /home/olivier/.spamassassin/auto-whitelist.lock: Permission denied To solve this, the .spamassassin
directory of all my users (to be created eventually) belongs to the mail user or set the rights to 777. Note that AWL (autowhitelist) allows you to put a score on the email addresses you use the most to better distinguish your usual contacts from the others.
init.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URIDNSBL
init.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::SPF
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DCC
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Pyzor
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Razor2
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::SpamCop
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AntiVirus
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AWL
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AutoLearnThreshold
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::TextCat
v310.pre:#loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AccessDB
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::WhiteListSubject
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::MIMEHeader
v310.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ReplaceTags
v312.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DKIM
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Check
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HTTPSMismatch
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URIDetail
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Shortcircuit
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Bayes
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::BodyEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DNSEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HTMLEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HeaderEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::MIMEEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::RelayEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URIEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::WLBLEval
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::VBounce
v320.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Rule2XSBody
v320.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ASN
v320.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ImageInfo
v330.pre:#loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::PhishTag
v330.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::FreeMail
v340.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::AskDNS
v341.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::TxRep
v341.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::URILocalBL
v341.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::PDFInfo
v342.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::HashBL
v342.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ResourceLimits
v342.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::FromNameSpoof
v342.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::Phishing
v343.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::OLEVBMacro
v400.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::ExtractText
v400.pre:# loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DecodeShortURLs
v400.pre:loadplugin Mail::SpamAssassin::Plugin::DMARC
Interfacing with sendmail
tar xvfz spamass-milter-0.4.0.tar.gz
This gives the directory spamass-milter-0.4.0 in which we type successively
./configure
make
Then as root
make install
First of all we must launch the SpamAssassin daemon as root
spamd -d -D -u mail -H /var/spool/mail
-d daemon mode
-D debug mode (optional, useful at the very beginning)
-u mail the mail user will be the owner of the process.
-H the directory where the Bayesian database is located
spamass-milter -u mail -p /var/run/spamass.sock -f
Now modify the sendmail configuration file , assuming that it is under /usr/share/sendmail-cf/cf and that it is called config.mc
cd /usr/share/sendmail-cf/cf
Add the following lines at the end
INPUT_MAIL_FILTER(`spamassassin', `S=local:/var/run/spamass.sock, F=, T=C:15m;S:4m;R:4m;E:10m')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_CONNECT',`t, b, j, _, {daemon_name}, {if_name}, {if_addr}')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_HELO',`s, {tls_version}, {cipher}, {cipher_bits}, {cert_subject}, {cert_issuer}')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_ENVFROM',`i, {auth_authen}, {auth_type}')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_ENVRCPT',`r, v, Z')dnl
# Milter options
#O Milter.LogLevel
O Milter.macros.connect=t, b, j, _, {daemon_name}, {if_name}, {if_addr}
O Milter.macros.helo=s, {tls_version}, {cipher}, {cipher_bits}, {cert_subject}, {cert_issuer}
O Milter.macros.envfrom=i, {auth_authen}, {auth_type}
O Milter.macros.envrcpt=r, v, Z
O Milter.macros.eom={msg_id}
#O Milter.macros.eoh
#O Milter.macros.data
# Milter options
#O Milter.LogLevel
O Milter.macros.connect=t, b, j, _, {daemon_name}, {if_name}, {if_addr}
O Milter.macros.helo=s, {tls_version}, {cipher}, {cipher_bits}, {cert_subject}, {cert_issuer}
O Milter.macros.envfrom=i
O Milter.macros.envfrom=i, {auth_authen}, {auth_type}
O Milter.macros.envrcpt=r, v, Z
O Milter.macros.eom={msg_id}
#O Milter.macros.eoh
#O Milter.macros.data
this modification is useful to avoid this kind of error
systemctl stop sendmail
systemctl start sendmail
Auto launch
For an automatic launch of spamd and spamass-milter we will create the file spamassassin.service which we place under /usr/lib/systemd/system/ here is its content[Unit]
Description=Spamassassin
daemon
After=syslog.target
network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/spamd
-d -D -u mail -H /var/spool/mail --pidfile
/var/run/spamd.pid
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
note that the -D option corresponds to
the optional debug mode, now for the service to be
launched at each boot of the machine you will have to
type
systemctl enable
spamassassin.service
here is the result
Created symlink from
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/spamassassin.service
to /usr/lib/systemd/system/spamassassin.service.
to launch it now just
type
systemctl start
spamassassin.service
Oct. 04 20:59:54 mana.kervao.fr spamd[1634]: config: no rules were found! Do you need to run 'sa-update'?
Oct. 04 20:59:55 mana.kervao.fr spamd[1516]: child process [1634] exited or timed out without signaling production of a PID file: exit 25...ne 2989. you will have to remember to type
sa-update
first this is what the following command gives systemctl status spamassassin
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/spamassassin.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2024-08-10 08:26:24 CEST; 5s ago
Process: 96542 ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/spamd -d -u mail -H /var/spool/mail --pidfile /var/run/spamd.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 96544 (spamd)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 9239)
Memory: 137.6M
CPU: 2.907s
CGroup: /system.slice/spamassassin.service
├─96544 spamd
├─96548 "spamd child"
└─96549 "spamd child"
août 10 08:26:21 ultra.kervao.fr systemd[1]: Starting spamassassin.service...
août 10 08:26:21 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96542]: logger: removing stderr method
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96544]: spamd: server started on IO::Socket::IP [::1]:783, IO::Socket::IP [127.0.0.1]:783 (running version 4.0.1)
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96544]: spamd: server pid: 96544
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96544]: spamd: server successfully spawned child process, pid 96548
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr systemd[1]: Started spamassassin.service.
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96544]: spamd: server successfully spawned child process, pid 96549
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96544]: prefork: child states: IS
août 10 08:26:24 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[96544]: prefork: child states: II
now let's move on to spamass-milter we will create the file spamass-milter.service under /usr/lib/systemd/system here is its content
[Unit]
Description = Mail filter for SpamAssassin
Wants = spamassassin.service
After = syslog.target local-fs.target network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target spamassassin.service
Before = sendmail.service
[Service]
Type = simple
ExecStart = /usr/local/sbin/spamass-milter -u mail -p /var/run/spamass.sock
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.target
now for the service to
be launched at each boot of the machine you will have to
type
systemctl enable
spamass-milter.service
here is the result
Created symlink from
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/spamass-milter.service
to /usr/lib/systemd/system/spamass-milter.service.
to launch it now just
type
systemctl start
spamass-milter.service
here is the result of the systemctl status spamass-milter.service command
●
spamass-milter.service - Mail filter for SpamAssassin
Loaded: loaded
(/usr/lib/systemd/system/spamass-milter.service;
enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running)
since Sat 2021-09-11 14:08:35 CEST; 5h 15min ago
Main
PID: 2094 (spamass-milter)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4677)
Memory: 552.0K
CPU: 126ms
CGroup:
/system.slice/spamass-milter.service
└─2094 /usr/local/sbin/spamass-milter -u mail -p
/var/run/spamass.sock
Sep 11 14:08:35
mana.kervao.fr systemd[1]: Started Mail filter for
SpamAssassin.
Sep 11 14:08:35
mana.kervao.fr spamass-milter[2094]: spamass-milter
0.4.0 starting
Functionning
Spam handling
Here are two techniques to take into account spamProcmail Technique
Now I created a .procmailrc file under my homedirectory which contains
:0fw: spamassassin.lock
* < 256000
| spamassassin
:0:
* ^X-Spam-Status: Yes
caughtspam
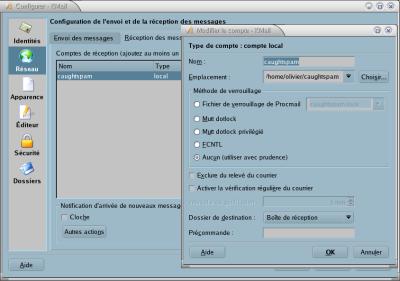
You do not create this .procmailrc file however in your account configuration in the spam settings.
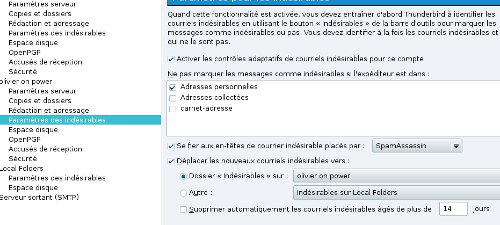
/home/user/.spamassasin/user_prefswhitelist_from *@ldlc.fr *@rueducommerce.com *@fnac.com
The lists will be common to all users and saved in the file /etc/mail/spamassassin/local.cf . Be careful, for the global file to be taken into account, you will have to delete the user_prefs file . It is not ideal to have to add these lists to the local.cf file , so I placed them in a file /etc/mail/spamassassin/white-black-list.cf . Small downside, the modifications of this file are only taken into account by restarting SpamAssassin and not dynamically.
More info about SpamAssassin configuration file here http://spamassassin.org/doc/Mail_SpamAssassin_Conf.html
In addition to the manual method, there is an automatic classification method called auto-whitelist which is based on certain algorithms (see here https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/SPAMASSASSIN/AutoWhitelist ). The database of this method is saved in the auto-whitelist file which is located under .spamassassin of each user. To see what is in it you will have to type
sa-awl ~/.spamassassin/auto-whitelist
it will give
something like this (extract)
12.3
(12.3/1) --
antoine-poirier@vme-147.com|ip=37.59
15.3
(15.3/1) -- edm@e8.zonfrontek.com|ip=70.39
28.9
(28.9/1) --
geykrapulyngalwyan@outlook.com|ip=37.207
16.8
(16.8/1) -- hicks+1761@bdis.fr|ip=79.247
14.8
(14.8/1) --
investissement-residence-service-211748@vme-uyt.com|ip=81.93
11.3
(22.6/2) --
mail6@nouvelle-vision.net|ip=178.33
15.1
(15.1/1) --
mutuelle_senior@cible-directe.fr|ip=185.52
10.0
(20.0/2) --
news@unmailundeal.com|ip=212.18
2.0
(6.1/3) --
newsletter@mabellephoto.com|ip=85.158
12.7
(12.7/1) --
protection@news7.sedem.info|ip=5.135
4.9
(4.9/1) -- abidjahan9@gmail.com|ip=209.85
4.6
(4.6/1) -- automated@e.airbnb.com|ip=199.7
7.2
(28.7/4) -- bcastuae@gmail.com|ip=110.36
17.9
(17.9/1) -- contact@efsr26.info|ip=37.59
11.0
(11.0/1) -- contact@infos-pro.com|ip=8.8
The first number is the average score, in parentheses the first corresponds to the total score of the emails and the second the number of emails concerned. To delete an email from the list, type
spamassassin --remove-addr-from-whitelist=foo@bar
the following command will remove entries viewed less than three times
sa-awl --clean --min 3 ~/.spamassassin/auto-whitelist
août 10 10:16:03 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[97375]: spamd: processing message <20240809201546.4FFA3B4A28658309@easywealthmgt.com> for olivier:8
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[97375]: async: aborting after 4.654 s, deadline shrunk: AskDNS, A/easywealthmgt.com.fresh.fmb.la, rules: __FROM_FMBLA_NEWDOM14, __FROM_FMBLA_NEWDOM28, __FROM_FMBLA_NEWDOM, __FROM_FMBLA_NDBLOCKED
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[97375]: spamd: identified spam (17.4/5.0) for olivier:8 in 4.7 seconds, 3679 bytes.
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[97375]: spamd: result: Y 17 - ADVANCE_FEE_3_NEW_FRM_MNY,DKIM_ADSP_NXDOMAIN,DMARC_MISSING,FILL_THIS_FORM,FILL_THIS_FORM_LOAN,FILL_THIS_FORM_LONG,HTML_MESSAGE,LOTS_OF_MONEY,MILLION_USD,MIME_HTML_ONLY,MONEY_FORM,MONEY_FRAUD_3,RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET,RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_BL,RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_L5,RCVD_IN_PBL,RCVD_IN_SBL_CSS,RCVD_IN_VALIDITY_RPBL,RCVD_IN_XBL,RDNS_NONE scantime=4.7,size=3679,user=olivier,uid=8,required_score=5.0,rhost=localhost,raddr=::1,rport=57010,mid=<20240809201546.4FFA3B4A28658309@easywealthmgt.com>,autolearn=no autolearn_force=no
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899: Milter (spamassassin) add: header: X-Spam-Status: Yes, score=17.4 required=5.0 tests=ADVANCE_FEE_3_NEW_FRM_MNY,\n\tDKIM_ADSP_NXDOMAIN,DMARC_MISSING,FILL_THIS_FORM,FILL_THIS_FORM_LOAN,\n\tFILL_THIS_FORM_LONG,HTML_MESSAGE,LOTS_OF_MONEY,MILLION_USD,\n\tMIME_HTML_ONLY,MONEY_FORM,MONEY_FRAUD_3,RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET,\n\tRCVD_IN_MSPIKE_BL,RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_L5,RCVD_IN_PBL,RCVD_IN_SBL_CSS,\n\tRCVD_IN_VALIDITY_RPBL,RCVD_IN_XBL,RDNS_NONE autolearn=no\n\tautolearn_force=no version=4.0.1
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899[1]: Milter (spamassassin) delete: header X-Spam-Report: \n\t* 1.2 RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET RBL: Received via a relay in\n\t* bl.spamcop.net\n\t* [Blocked - see <https://www.spamcop.net/bl.shtml?139.99.220.252>]\n\t* 2.7 RCVD_IN_PSBL RBL: Received via a relay in PSBL\n\t* [139.99.220.252 listed in psbl.surriel.com]\n\t* 3.6 RCVD_IN_SBL_CSS RBL: Received via a relay in Spamhaus SBL-CSS\n\t* [139.99.220.252 listed in zen.spamhaus.org]\n\t* 3.6 RCVD_IN_PBL RBL: Received via a relay in Spamhaus PBL\n\t* 0.7 RCVD_IN_XBL RBL: Received via a relay in Spamhaus XBL\n\t* 0.8 DKIM_ADSP_NXDOMAIN No valid author signature and domain not in\n\t* DNS\n\t* 0.1 MIME_HTML_ONLY BODY: Message only has text/html MIME parts\n\t* 0.0 HTML_MESSAGE BODY: HTML included in message\n\t* 2.5 RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_L5 RBL: Very bad reputation (-5)\n\t* [139.99.220.252 listed in bl.mailspike.net]\n\t* 1.3 RCVD_IN_RP_RNBL RBL: Relay in RNBL,\n\t* ...
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899[2]: https://senderscore.org/blacklistlookup/\n\t* [139.99.220.252 listed in bl.score.senderscore.com]\n\t* -3.0 RCVD_IN_RP_CERTIFIED RBL: Sender in ReturnPath Certified -\n\t* Contact cert-sa@returnpath.net\n\t* [Excessive Number of Queries | <https://knowledge.validity.com/hc/en-us/articles/20961730681243>]\n\t* -2.0 RCVD_IN_RP_SAFE RBL: Sender in ReturnPath Safe - Contact\n\t* safe-sa@returnpath.net\n\t* 1.3 RDNS_NONE Delivered to internal network by a host with no rDNS\n\t* 0.0 LOTS_OF_MONEY Huge... sums of money\n\t* 0.0 RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_BL Mailspike blacklisted\n\t* 1.0 HELO_MISC_IP Looking for more Dynamic IP Relays\n\t* 0.0 FILL_THIS_FORM Fill in a form with personal information\n\t* 2.0 FILL_THIS_FORM_LONG Fill in a form with personal information\n\t* 0.0 T_FILL_THIS_FORM_LOAN Answer loan question(s)\n\t* 1.0 MONEY_FORM Lots of money if you fill out a form\n\t* 1.0 MONEY_FRAUD_3 Lots of money and several fraud ...
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899[3]: phrases
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899: Milter (spamassassin) add: header: X-Spam-Level: *****************
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899: Milter (spamassassin) change: header X-Spam-Checker-Version: from SpamAssassin 3.4.4 (2020-01-24) on\n\tpar1-wbh-prd-eximproxy02.internal.scaleway.com to SpamAssassin 4.0.1 (2024-03-26) on ultra.kervao.fr
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899: Milter (spamassassin) change: header Content-Type: from text/html;\n\tcharset="iso-8859-1" to multipart/mixed; boundary="----------=_66B721C7.18CD7D78"
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[101899]: 47A8G0Eu101899: Milter (spamassassin) message: body replaced
août 10 10:16:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[97371]: prefork: child states: II
Message-Id: <NngOtqW.56902.970.JDT@litcharts.com>
Date: Sun, 11 Aug 2024 07:45:37 +0200
MIME-Version: 1.0
Subject: *****SPAM***** Sie sich Anfang August-Geschenk🔥
Reply-To: reply_to@litcharts.com
To: olivier.hoarau@funix.org
Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary="----------=_66B889AF.9A4D3319"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit
X-online-proxy-in: FLEX_RVVNa01vc1lvVXlReUE4Sw==EOHC2hIK3H6k4v9o4asxECWLUUNEt7LA
X-online-to: olivier.hoarau@funix.org
X-original-for: olivier.hoarau@funix.org
X-Virus-Scanned: clamav-milter 1.2.0 at ultra.kervao.fr
X-Virus-Status: Clean
X-Spam-Flag: YES
X-Spam-Status: Yes, score=23.7 required=5.0 tests=AMAZON_IMG_NOT_RCVD_AMZN,
BAYES_99,BAYES_999,DCC_CHECK,DCC_REPUT_99_100,DIGEST_MULTIPLE,
DMARC_NONE,FONT_INVIS_MSGID,FSL_BULK_SIG,HOSTED_IMG_DIRECT_MX,
HTML_FONT_TINY_NORDNS,HTML_IMAGE_RATIO_08,HTML_MESSAGE,MIME_HTML_ONLY,
RAZOR2_CF_RANGE_51_100,RAZOR2_CHECK,RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET,
RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_BL,RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_ZBI,RCVD_IN_SBL_CSS,RDNS_NONE,
SPF_HELO_NEUTRAL,T_REMOTE_IMAGE,URIBL_DBL_SPAM shortcircuit=no
autolearn=spam autolearn_force=no version=4.0.1
X-Spam-Level: ***********************
X-Spam-Checker-Version: SpamAssassin 4.0.1 (2024-03-26) on ultra.kervao.fr
This is a multi-part message in MIME format.
------------=_66B889AF.9A4D3319
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1
Content-Disposition: inline
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit
------------------ Début de Rapport SpamAssassin ---------------------
Ce message est probablement du SPAM (message non sollicité envoyé en
masse, publicité, escroquerie...).
Cette notice a été ajoutée par le système d'analyse "SpamAssassin" sur
votre serveur de courrier "ultra.kervao.fr", pour vous
aider à identifier ce type de messages.
Le système SpamAssassin ajoute un en-tête "X-Spam-Flag: YES" aux
messages qu'il considère comme étant probablement du Spam.
Vous pouvez si vous le souhaitez utiliser cette caractéristique
pour régler un filtre dans votre logiciel de lecture de courrier,
afin de détruire ou de classer à part ce type de message.
Si ce robot a classifié incorrectement un message qui vous était
destiné, ou pour toute question, veuillez contacter l'administrateur
du système par e-mail à olivier .
Voir https://spamassassin.apache.org/tag/ pour plus de détails (en anglais).
Détails de l'analyse du message: (23.7 points, 5.0 requis)
1.3 RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET RBL: Relais listé dans
http://spamcop.net/bl.shtml
[Blocked - see <https://www.spamcop.net/bl.shtml?23.228.85.170>]
3.3 RCVD_IN_SBL_CSS RBL: Received via a relay in Spamhaus SBL-CSS
[23.228.85.170 listed in zen.spamhaus.org]
2.5 URIBL_DBL_SPAM Contains a spam URL listed in the Spamhaus DBL
blocklist
[URI: www.addimprovement.bumbleshrimp.com]
0.1 SPF_HELO_NEUTRAL SPF: HELO does not match SPF record (neutral)
1.1 DCC_CHECK Message listé par DCC: http://www.www.dcc-servers.net/dcc/
0.0 RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_BL Mailspike blocklisted
0.0 RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_ZBI No description available.
0.1 DMARC_NONE DMARC none policy
3.5 BAYES_99 BODY: L'algorithme Bayésien a évalué la probabilité de spam
entre 99 et 100%
[score: 1.0000]
0.2 BAYES_999 BODY: L'algorithme Bayésien a évalué la probabilité de spam
entre 99.9 et 100%
[score: 1.0000]
0.0 HTML_IMAGE_RATIO_08 BODY: HTML Faible ratio de texte par rapport aux
images
0.1 MIME_HTML_ONLY BODY: Le message possède uniquement des parties MIME
text/html
0.0 HTML_MESSAGE BODY: HTML inclus dans le message
0.8 RDNS_NONE Delivered to internal network by a host with no rDNS
2.0 HTML_FONT_TINY_NORDNS Font too small to read, no rDNS
2.2 AMAZON_IMG_NOT_RCVD_AMZN Amazon hosted image but message not from
Amazon
1.9 FONT_INVIS_MSGID Invisible text + suspicious message ID
0.0 HOSTED_IMG_DIRECT_MX Image hosted at large ecomm, CDN or hosting
site, message direct-to-mx
0.0 T_REMOTE_IMAGE Message contains an external image
1.4 DCC_REPUT_99_100 DCC reputation between 99 % or higher (spam)
0.9 RAZOR2_CHECK Message listé par Razor2, voir
http://razor.sourceforge.net
1.9 RAZOR2_CF_RANGE_51_100 Razor2 donne un indice de confiance entre 51
et 100
[cf: 100]
0.0 FSL_BULK_SIG Bulk signature with no Unsubscribe
0.3 DIGEST_MULTIPLE Message hits more than one network digest check
-------------------- Fin de Rapport SpamAssassin ---------------------
Each email receives the following information in the header style (for spam)
DKIM_ADSP_NXDOMAIN,DMARC_MISSING,FILL_THIS_FORM,FILL_THIS_FORM_LOAN,
FILL_THIS_FORM_LONG,HTML_MESSAGE,LOTS_OF_MONEY,MILLION_USD,
MIME_HTML_ONLY,MONEY_FORM,MONEY_FRAUD_3,RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET,
RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_BL,RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_L5,RCVD_IN_PBL,RCVD_IN_SBL_CSS,
RCVD_IN_VALIDITY_RPBL,RCVD_IN_XBL,RDNS_NONE autolearn=no
autolearn_force=no version=4.0.1
X-Spam-Level: *****************
DKIM_VALID_AU,DMARC_PASS,HTML_MESSAGE,RCVD_IN_DNSWL_NONE,
RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_H5,RCVD_IN_MSPIKE_WL,RDNS_NONE,SPF_HELO_NONE,
T_REMOTE_IMAGE,USER_IN_WELCOMELIST autolearn=no autolearn_force=no
version=4.0.1
X-Spam-Checker-Version: SpamAssassin 4.0.1 (2024-03-26) on ultra.kervao.fr
(locale config)
X-Spam-Status: Yes, score=11.7 required=5.0 tests=BAYES_40,DKIM_SIGNED,
DKIM_VALID,DKIM_VALID_AU,DKIM_VALID_EF,FREEMAIL_ENVFROM_END_DIGIT,
FREEMAIL_FROM,HTML_MESSAGE,NO_RDNS_DOTCOM_HELO,RCVD_IN_DNSWL_NONE,
RDNS_NONE,SPF_HELO_NONE,UNWANTED_LANGUAGE_BODY shortcircuit=no
autolearn=no autolearn_force=no version=4.0.1
X-Spam-Level: ***********
0.0 SHORTCIRCUIT Not all rules were run, due to a shortcircuited
rule
100 USER_IN_BLOCKLIST From: address is in the user's black-list
USER_IN_WHITELIST,USER_IN_WELCOMELIST shortcircuit=ham
autolearn=disabled version=4.0.1
sa-learn --ham --dir /home/olivier/.Mail/fauxspam/cur
/usr/local/bin/sa-learn --ham --dir /export/home/user/fauxspams
/usr/local/bin/sa-learn --spam --dir /export/home/user/spams
Here is the result
Learned from 3 message(s) (3 message(s) examined).
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/bin/sa-learn --ham --dir /export/home/user1/fauxspams
/usr/local/bin/sa-learn --spam --dir /export/home/user1/spams
/usr/local/bin/sa-learn --ham --dir /export/home/user2/fauxspams
/usr/local/bin/sa-learn --spam --dir /export/home/user2/spams
And give it execution rights
chmod 755 /etc/cron.daily/bayes
0.000 0 9041 0 non-token data: nspam
0.000 0 12164 0 non-token data: nham
0.000 0 171108 0 non-token data: ntokens
0.000 0 1603119662 0 non-token data: oldest atime
0.000 0 1605952921 0 non-token data: newest atime
0.000 0 1605952891 0 non-token data: last journal sync atime
0.000 0 1605927677 0 non-token data: last expired atime
0.000 0 2764800 0 non-token data: last expire atime delta
0.000 0 3481 0 non-token data: last expire reduction count
Feb. 23 11:58:10 mana.kervao.fr spamd[1635]: dns: sendto() to [::1]:53 failed: Connection refused, failing over to [127.0.0.1]:53
Feb. 23 11:58:10 mana.kervao.fr spamd[1635]: dns: bad dns reply: bgread: recv() failed: Connection refused at /usr/local/share/perl5/Mail/SpamAssassin/DnsResolver.pm line 742, <GEN353> line 525.
Feb. 23 11:58:10 mana.kervao.fr spamd[1635]: dns: bad dns reply: bgread: recv() failed: Connection refused at /usr/local/share/perl5/Mail/SpamAssassin/DnsResolver.pm line 742.
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP2: city database not found from default locations
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP2: country database not found from default locations
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: versions: Geo::IP 1.51, C library 1.6.12
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: search found city /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: search found city
/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCityv6.dat
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: search found country /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIP.dat
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: search found country /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIPv6.dat
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: loaded city from /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
GeoIP: loaded country from /usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIP.dat
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
database info: Geo::IP IPv4 city: GEO-533LITE 20180327
Build 1 Copyright (c) 2018 MaxMind Inc All Rights R>
août 11 10:28:14 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[359354]: geodb:
database info: Geo::IP IPv4 country: GEO-106FREE 20180327
Build 1 Copyright (c) 2018 MaxMind Inc All Right>
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: dkim: performing public ARC key lookup and signature verification
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: dkim: ARC signature verification result: none
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: dkim: adsp not retrieved, author domain signature is valid
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: dkim: adsp result: - (valid a. d. signature), author domain 'news.leboncoin.fr'
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: spf: welcomelist_from_spf: already checked spf and didn't get pass, skipping welcomelist check
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: dkim: VALID signature by news.leboncoin.fr, author info@news.leboncoin.fr, no valid matches
août 11 13:22:07 ultra.kervao.fr spamd[422090]: dkim: author info@news.leboncoin.fr, not in any dkim welcomelist
Install an anti virus
tar xvfz clamav-1.3.1.tar.gz
This gives clamav-1.3.1 before going further you can recover the very good documentation available at this location http://wiki.clamav.net/Main/WebHome. By following the instructions we must first as root create a user clamav
useradd -g clamav -s /bin/false -c "Clam Anti Virus" clamav
Then as a simple user in the clamav-1.3.1 directory we must type
Package Version: ClamAV 1.3.1
libclamav version: 12:2:0
libfreshclam version: 3:1:0
Install prefix: /usr/local
Install database dir: /usr/local/share/clamav
Install config dir: /usr/local/etc
Host system: Linux-6.6.43-desktop-1.mga9
Target system: Linux-6.6.43-desktop-1.mga9
Compiler:
Build type: RelWithDebInfo
C compiler: /usr/bin/cc
C++ compiler: /usr/bin/c++
Rust toolchain: /usr/bin/cargo (1.74.0)
CFLAGS: -O2 -g
CXXFLAGS: -O2 -g
WARNCFLAGS: -Wall -Wextra -Wformat-security
Build Options:
Build apps: ON
Shared library: ON
Static library: OFF
Enable UnRAR: ON
Examples: OFF
Tests: ON
Build man pages: ON
Build doxygen HTML: OFF
Maintainer Mode: OFF
Build Extras:
Build milter: ON (toggle with -DENABLE_MILTER=ON/OFF)
Build clamonacc: ON (toggle with -DENABLE_CLAMONACC=ON/OFF)
-- Engine Options --
Bytecode Runtime:
interpreter
-- Test Dependencies --
Unit Test Framework:
libcheck /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libcheck.so
Feature Test Framework:
python3 /usr/bin/python3.10
test command pytest;-v
-- libclamav Dependencies --
Compression support:
bzip2 /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libbz2.so
zlib /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libz.so
XML support:
libxml2 /usr/include/libxml2;/usr/include/libxml2
/usr/lib64/libxml2.so
RegEx support:
libpcre2 /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libpcre2-8.so
Crypto support:
openssl /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libssl.so;/usr/lib64/libcrypto.so
JSON support:
json-c /usr/include/json-c
/usr/lib64/libjson-c.so
Threading support:
pthread
Locale support:
iconv /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libc.so
-- libfreshclam Extra Dependencies --
HTTP support:
curl /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libcurl.so
-- Application Extra Dependencies --
GUI support:
ncurses /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libncurses.so;/usr/lib64/libtinfo.so
systemd:
unit directory /usr/lib/systemd/system
systemd ctl support:
libsystemd /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libsystemd.so
Milter Support:
libmilter /usr/include
/usr/lib64/libmilter.so
-- Warning: libjson-c is known to share symbol names with other JSON libraries which may result in crashes for applications that use libclamav. Consider providing a static json-c library that was compiled with: CFLAGS="-fPIC". Default build settings for json-c 0.15+ should also work. Use the `-DENABLE_JSON_SHARED=OFF` option to prefer detection of the static library, or use -DJSONC_INCLUDE_DIR and -DJSONC_LIBRARY to specify the static JSON library.
-- Configuring done (24.8s)
-- Generating done (0.2s)
-- Build files have been written to: /usr/local/linux/mail/clamav-1.3.1/build
make install
We add if it is not already done the line /usr/local/lib (and /usr/local/lib64 for a 64bit version) in the file /etc/ld.so.conf and we type
ldconfig
Now we create the clamav log directory, the clamav user must be the owner
mkdir /var/log/clamav
chown clamav:clamav /var/log/clamav
Configuration
We edit the file /usr/local/etc/clamd.conf here is how I configured it##
## Example config file for the Clam AV daemon
## Please read the clamd.conf(5) manual before editing this file.
##
# Comment or remove the line below.
#Example
# Uncomment this option to enable logging.
# LogFile must be writable for the user running daemon.
# A full path is required.
# Default: disabled
#LogFile /tmp/clamd.log
LogFile /var/log/clamav/clamd.log
# By default the log file is locked for writing - the lock protects against
# running clamd multiple times (if want to run another clamd, please
# copy the configuration file, change the LogFile variable, and run
# the daemon with --config-file option).
# This option disables log file locking.
# Default: no
#LogFileUnlock yes
# Maximum size of the log file.
# Value of 0 disables the limit.
# You may use 'M' or 'm' for megabytes (1M = 1m = 1048576 bytes)
# and 'K' or 'k' for kilobytes (1K = 1k = 1024 bytes). To specify the size
# in bytes just don't use modifiers. If LogFileMaxSize is enabled, log
# rotation (the LogRotate option) will always be enabled.
# Default: 1M
LogFileMaxSize 2M
# Log time with each message.
# Default: no
#LogTime yes
# Also log clean files. Useful in debugging but drastically increases the
# log size.
# Default: no
#LogClean yes
# Use system logger (can work together with LogFile).
# Default: no
#LogSyslog yes
# Specify the type of syslog messages - please refer to 'man syslog'
# for facility names.
# Default: LOG_LOCAL6
#LogFacility LOG_MAIL
# Enable verbose logging.
# Default: no
#LogVerbose yes
# Enable log rotation. Always enabled when LogFileMaxSize is enabled.
# Default: no
#LogRotate yes
# Log additional information about the infected file, such as its
# size and hash, together with the virus name.
#ExtendedDetectionInfo yes
# This option allows you to save a process identifier of the listening
# daemon (main thread).
# Default: disabled
PidFile /var/log/clamav/clamd.pid
# Optional path to the global temporary directory.
# Default: system specific (usually /tmp or /var/tmp).
TemporaryDirectory /tmp
# Path to the database directory.
# Default: hardcoded (depends on installation options)
DatabaseDirectory /usr/local/share/clamav
# Only load the official signatures published by the ClamAV project.
# Default: no
#OfficialDatabaseOnly no
# The daemon can work in local mode, network mode or both.
# Due to security reasons we recommend the local mode.
# Path to a local socket file the daemon will listen on.
# Default: disabled (must be specified by a user)
#LocalSocket /tmp/clamd.socket
LocalSocket /var/log/clamav/clamd.sock
# Sets the group ownership on the unix socket.
# Default: disabled (the primary group of the user running clamd)
#LocalSocketGroup virusgroup
# Sets the permissions on the unix socket to the specified mode.
# Default: disabled (socket is world accessible)
#LocalSocketMode 660
# Remove stale socket after unclean shutdown.
# Default: yes
FixStaleSocket yes
# TCP port address.
# Default: no
#TCPSocket 3310
# TCP address.
# By default we bind to INADDR_ANY, probably not wise.
# Enable the following to provide some degree of protection
# from the outside world. This option can be specified multiple
# times if you want to listen on multiple IPs. IPv6 is now supported.
# Default: no
#TCPAddr 127.0.0.1
# Maximum length the queue of pending connections may grow to.
# Default: 200
#MaxConnectionQueueLength 30
# Clamd uses FTP-like protocol to receive data from remote clients.
# If you are using clamav-milter to balance load between remote clamd daemons
# on firewall servers you may need to tune the options below.
# Close the connection when the data size limit is exceeded.
# The value should match your MTA's limit for a maximum attachment size.
# Default: 25M
#StreamMaxLength 10M
# Limit port range.
# Default: 1024
#StreamMinPort 30000
# Default: 2048
#StreamMaxPort 32000
# Maximum number of threads running at the same time.
# Default: 10
MaxThreads 20
# Waiting for data from a client socket will timeout after this time (seconds).
# Default: 120
ReadTimeout 300
# This option specifies the time (in seconds) after which clamd should
# timeout if a client doesn't provide any initial command after connecting.
# Default: 5
#CommandReadTimeout 5
# This option specifies how long to wait (in miliseconds) if the send buffer is full.
# Keep this value low to prevent clamd hanging
#
# Default: 500
#SendBufTimeout 200
# Maximum number of queued items (including those being processed by MaxThreads threads)
# It is recommended to have this value at least twice MaxThreads if possible.
# WARNING: you shouldn't increase this too much to avoid running out of file descriptors,
# the following condition should hold:
# MaxThreads*MaxRecursion + (MaxQueue - MaxThreads) + 6< RLIMIT_NOFILE (usual max is 1024)
#
# Default: 100
#MaxQueue 200
# Waiting for a new job will timeout after this time (seconds).
# Default: 30
#IdleTimeout 60
# Don't scan files and directories matching regex
# This directive can be used multiple times
# Default: scan all
#ExcludePath ^/proc/
#ExcludePath ^/sys/
# Maximum depth directories are scanned at.
# Default: 15
#MaxDirectoryRecursion 20
# Follow directory symlinks.
# Default: no
#FollowDirectorySymlinks yes
# Follow regular file symlinks.
# Default: no
#FollowFileSymlinks yes
# Scan files and directories on other filesystems.
# Default: yes
#CrossFilesystems yes
# Perform a database check.
# Default: 600 (10 min)
#SelfCheck 600
# Execute a command when virus is found. In the command string %v will
# be replaced with the virus name.
# Default: no
#VirusEvent /usr/local/bin/send_sms 123456789 "VIRUS ALERT: %v"
# Run as another user (clamd must be started by root for this option to work)
# Default: don't drop privileges
User clamav
# Initialize supplementary group access (clamd must be started by root).
# Default: no
#AllowSupplementaryGroups no
# Stop daemon when libclamav reports out of memory condition.
#ExitOnOOM yes
# Don't fork into background.
# Default: no
Foreground yes
# Enable debug messages in libclamav.
# Default: no
# Debug yes
# Do not remove temporary files (for debug purposes).
# Default: no
#LeaveTemporaryFiles yes
# Permit use of the ALLMATCHSCAN command. If set to no, clamd will reject
# any ALLMATCHSCAN command as invalid.
# Default: yes
#AllowAllMatchScan no
# Detect Possibly Unwanted Applications.
# Default: no
#DetectPUA yes
# Exclude a specific PUA category. This directive can be used multiple times.
# See https://github.com/vrtadmin/clamav-faq/blob/master/faq/faq-pua.md for
# the complete list of PUA categories.
# Default: Load all categories (if DetectPUA is activated)
#ExcludePUA NetTool
#ExcludePUA PWTool
# Only include a specific PUA category. This directive can be used multiple
# times.
# Default: Load all categories (if DetectPUA is activated)
#IncludePUA Spy
#IncludePUA Scanner
#IncludePUA RAT
# In some cases (eg. complex malware, exploits in graphic files, and others),
# ClamAV uses special algorithms to provide accurate detection. This option
# controls the algorithmic detection.
# Default: yes
AlgorithmicDetection yes
# This option causes memory or nested map scans to dump the content to disk.
# If you turn on this option, more data is written to disk and is available
# when the LeaveTemporaryFiles option is enabled.
#ForceToDisk yes
# This option allows you to disable the caching feature of the engine. By
# default, the engine will store an MD5 in a cache of any files that are
# not flagged as virus or that hit limits checks. Disabling the cache will
# have a negative performance impact on large scans.
# Default: no
#DisableCache yes
##
## Executable files
##
# PE stands for Portable Executable - it's an executable file format used
# in all 32 and 64-bit versions of Windows operating systems. This option allows
# ClamAV to perform a deeper analysis of executable files and it's also
# required for decompression of popular executable packers such as UPX, FSG,
# and Petite. If you turn off this option, the original files will still be
#scanned, but without additional processing.
# Default: yes
ScanPE yes
# Certain PE files contain an authenticode signature. By default, we check
# the signature chain in the PE file against a database of trusted and
# revoked certificates if the file being scanned is marked as a virus.
# If any certificate in the chain validates against any trusted root, but
# does not match any revoked certificate, the file is marked as whitelisted.
# If the file does match a revoked certificate, the file is marked as virus.
# The following setting completely turns off authenticode verification.
# Default: no
#DisableCertCheck yes
# Executable and Linking Format is a standard format for UN*X executables.
# This option allows you to control the scanning of ELF files.
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without additional processing.
# Default: yes
ScanELF yes
##
## Documents
##
# This option enables scanning of OLE2 files, such as Microsoft Office
# documents and .msi files.
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without additional processing.
# Default: yes
ScanOLE2 yes
# With this option enabled OLE2 files with VBA macros, which were not
# detected by signatures will be marked as "Heuristics.OLE2.ContainsMacros".
# Default: no
#OLE2BlockMacros no
# This option enables scanning within PDF files.
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without decoding and additional processing.
# Default: yes
ScanPDF yes
# This option enables scanning within SWF files.
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without decoding and additional processing.
# Default: yes
ScanSWF yes
##
## Mail files
##
# Enable internal e-mail scanner.
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without parsing individual messages/attachments.
# Default: yes
ScanMail yes
# Scan RFC1341 messages split over many emails.
# You will need to periodically clean up $TemporaryDirectory/clamav-partial directory.
# WARNING: This option may open your system to a DoS attack.
# Never use it on loaded servers.
# Default: no
ScanPartialMessages yes
# With this option enabled ClamAV will try to detect phishing attempts by using
# signatures.
# Default: yes
PhishingSignatures yes
# Scan URLs found in mails for phishing attempts using heuristics.
# Default: yes
PhishingScanURLs yes
# Always block SSL mismatches in URLs, even if the URL isn't in the database.
# This can lead to false positives.
#
# Default: no
#PhishingAlwaysBlockSSLMismatch no
# Always block cloaked URLs, even if URL isn't in database.
# This can lead to false positives.
#
# Default: no
#PhishingAlwaysBlockCloak no
# Detect partition intersections in raw disk images using heuristics.
# Default: no
#PartitionIntersection no
# Allow heuristic match to take precedence.
# When enabled, if a heuristic scan (such as phishingScan) detects
# a possible virus/phish it will stop scan immediately. Recommended, saves CPU
# scan-time.
# When disabled, virus/phish detected by heuristic scans will be reported only at
# the end of a scan. If an archive contains both a heuristically detected
# virus/phish, and a real malware, the real malware will be reported
#
# Keep this disabled if you intend to handle "*.Heuristics.*" viruses
# differently from "real" malware.
# If a non-heuristically-detected virus (signature-based) is found first,
# the scan is interrupted immediately, regardless of this config option.
#
# Default: no
#HeuristicScanPrecedence yes
##
## Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
##
# Enable the DLP module
# Default: No
#StructuredDataDetection yes
# This option sets the lowest number of Credit Card numbers found in a file
# to generate a detect.
# Default: 3
#StructuredMinCreditCardCount 5
# This option sets the lowest number of Social Security Numbers found
# in a file to generate a detect.
# Default: 3
#StructuredMinSSNCount 5
# With this option enabled the DLP module will search for valid
# SSNs formatted as xxx-yy-zzzz
# Default: yes
#StructuredSSNFormatNormal yes
# With this option enabled the DLP module will search for valid
# SSNs formatted as xxxyyzzzz
# Default: no
#StructuredSSNFormatStripped yes
##
## HTML
##
# Perform HTML normalisation and decryption of MS Script Encoder code.
# Default: yes
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without additional processing.
#ScanHTML yes
##
## Archives
##
# ClamAV can scan within archives and compressed files.
# If you turn off this option, the original files will still be scanned, but
# without unpacking and additional processing.
# Default: yes
ScanArchive yes
# Mark encrypted archives as viruses (Encrypted.Zip, Encrypted.RAR).
# Default: no
#ArchiveBlockEncrypted no
##
## Limits
##
# The options below protect your system against Denial of Service attacks
# using archive bombs.
# This option sets the maximum amount of data to be scanned for each input file.
# Archives and other containers are recursively extracted and scanned up to this
# value.
# Value of 0 disables the limit
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 100M
#MaxScanSize 150M
# Files larger than this limit won't be scanned. Affects the input file itself
# as well as files contained inside it (when the input file is an archive, a
# document or some other kind of container).
# Value of 0 disables the limit.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 25M
#MaxFileSize 30M
# Nested archives are scanned recursively, e.g. if a Zip archive contains a RAR
# file, all files within it will also be scanned. This options specifies how
# deeply the process should be continued.
# Note: setting this limit too high may result in severe damage to the system.
# Default: 16
#MaxRecursion 10
# Number of files to be scanned within an archive, a document, or any other
# container file.
# Value of 0 disables the limit.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 10000
#MaxFiles 15000
# Maximum size of a file to check for embedded PE. Files larger than this value
# will skip the additional analysis step.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 10M
#MaxEmbeddedPE 10M
# Maximum size of a HTML file to normalize. HTML files larger than this value
# will not be normalized or scanned.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 10M
#MaxHTMLNormalize 10M
# Maximum size of a normalized HTML file to scan. HTML files larger than this
# value after normalization will not be scanned.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 2M
#MaxHTMLNoTags 2M
# Maximum size of a script file to normalize. Script content larger than this
# value will not be normalized or scanned.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 5M
#MaxScriptNormalize 5M
# Maximum size of a ZIP file to reanalyze type recognition. ZIP files larger
# than this value will skip the step to potentially reanalyze as PE.
# Note: disabling this limit or setting it too high may result in severe damage
# to the system.
# Default: 1M
#MaxZipTypeRcg 1M
# This option sets the maximum number of partitions of a raw disk image to be scanned.
# Raw disk images with more partitions than this value will have up to the value number
# partitions scanned. Negative values are not allowed.
# Note: setting this limit too high may result in severe damage or impact performance.
# Default: 50
#MaxPartitions 128
# This option sets the maximum number of icons within a PE to be scanned.
# PE files with more icons than this value will have up to the value number icons scanned.
# Negative values are not allowed.
# WARNING: setting this limit too high may result in severe damage or impact performance.
# Default: 100
#MaxIconsPE 200
##
## On-access Scan Settings
##
# Enable on-access scanning. Currently, this is supported via fanotify.
# Clamuko/Dazuko support has been deprecated.
# Default: no
#ScanOnAccess yes
# Don't scan files larger than OnAccessMaxFileSize
# Value of 0 disables the limit.
# Default: 5M
#OnAccessMaxFileSize 10M
# Set the include paths (all files inside them will be scanned). You can have
# multiple OnAccessIncludePath directives but each directory must be added
# in a separate line. (On-access scan only)
# Default: disabled
#OnAccessIncludePath /home
#OnAccessIncludePath /students
# Set the exclude paths. All subdirectories are also excluded.
# (On-access scan only)
# Default: disabled
#OnAccessExcludePath /home/bofh
# With this option you can whitelist specific UIDs. Processes with these UIDs
# will be able to access all files.
# This option can be used multiple times (one per line).
# Default: disabled
#OnAccessExcludeUID 0
##
## Bytecode
##
# With this option enabled ClamAV will load bytecode from the database.
# It is highly recommended you keep this option on, otherwise you'll miss detections for many new viruses.
# Default: yes
Bytecode yes
# Set bytecode security level.
# Possible values:
# None - no security at all, meant for debugging. DO NOT USE THIS ON PRODUCTION SYSTEMS
# This value is only available if clamav was built with --enable-debug!
# TrustSigned - trust bytecode loaded from signed .c[lv]d files,
# insert runtime safety checks for bytecode loaded from other sources
# Paranoid - don't trust any bytecode, insert runtime checks for all
# Recommended: TrustSigned, because bytecode in .cvd files already has these checks
# Note that by default only signed bytecode is loaded, currently you can only
# load unsigned bytecode in --enable-debug mode.
#
# Default: TrustSigned
#BytecodeSecurity TrustSigned
# Set bytecode timeout in miliseconds.
#
# Default: 5000
# BytecodeTimeout 1000
##
## Statistics gathering and submitting
##
# Enable statistical reporting.
# Default: no
#StatsEnabled yes
# Disable submission of individual PE sections for files flagged as malware.
# Default: no
#StatsPEDisabled yes
# HostID in the form of an UUID to use when submitting statistical information.
# Default: auto
#StatsHostID auto
# Time in seconds to wait for the stats server to come back with a response
# Default: 10
#StatsTimeout 10
The clamav-milter configuration file is called /usr/local/etc/clamav-milter.conf here it is, here are the lines I modified
#Example
MilterSocket /var/log/clamav/clmilter.sock
ClamdSocket unix:/var/log/clamav/clamd.sock
AddHeader Replace
LogFile /var/log/clamav/clamav-milter.log
for the rest everything is in comments
We now configure the file /usr/local/etc/freshclam.conf by commenting out the following line
#Example
Then by modifying the following line in accordance with what was defined in the clamd.conf file
# definition of the virus database
DatabaseDirectory /usr/local/share/clamav
I then modified the following lines
# definition of the freshclam log file
UpdateLogFile /var/log/clamav/freshclam.log
# mirror server to contact to retrieve updates oà day
DatabaseMirror db.fr.clamav.net
# database.clamav.net is a round-robin record which points to our most
# reliable mirrors. It's used as a fall back in case db.XY.clamav.net is
# not working. DO NOT TOUCH the following line unless you know what you
# are doing.
DatabaseMirror database.clamav.net
we will remember to first create the log files
touch /var/log/clamav/clamd.log
touch /var/log/clamav/freshclam.log
touch /var/log/clamav/clamav-milter.log
clamav must be the owner of the first two files
chown clamav:clamav /var/log/clamav/clamd.log
chown clamav:clamav /var/log/clamav/freshclam.log
we must first create the directory containing the virus database and clamav must own it
mkdir /usr/local/share/clamav
chown clamav:clamav /usr/local/share/clamav The
freshclam command allows you to update the database from information retrieved from the internet, as root type freshclam --datadir=/usr/local/share/clamav here is the result
daily database available for download (remote version: 27046)
Time: 1.4s, ETA: 0.0s [========================>] 58.97MiB/58.97MiB
Testing database: '/usr/local/share/clamav/tmp.9fe36bd938/clamav-3557261998181640b08c431851ade988.tmp-daily.cvd' ...
Database test passed.
daily.cvd updated (version: 27046, sigs: 2041850, f-level: 90, builder: raynman)
main database available for download (remote version: 62)
Time: 3.1s, ETA: 0.0s [========================>] 162.58MiB/162.58MiB
Testing database: '/usr/local/share/clamav/tmp.9fe36bd938/clamav-e27b8ca5d89e3bbf79e40fce342cd482.tmp-main.cvd' ...
Database test passed.
main.cvd updated (version: 62, sigs: 6647427, f-level: 90, builder: sigmgr)
bytecode database available for download (remote version: 334)
Time: 0.2s, ETA: 0.0s [========================>] 285.12KiB/285.12KiB
Testing database: '/usr/local/share/clamav/tmp.9fe36bd938/clamav-1d907c928e30a2ab4a04169388540564.tmp-bytecode.cvd' ...
Database test passed.
bytecode.cvd updated (version: 334, sigs: 91, f-level: 90, builder: anvilleg)
clamd
We will now do a test on the clamav-1.3.1 directory as a simple user clamscan -r -l log.txt clamav-1.3.1
Known viruses: 8697141
Engine version: 1.3.1
Scanned directories: 1966
Scanned files: 13624
Infected files: 52
Data scanned: 2676.77 MB
Data read: 2142.18 MB (ratio 1.25:1)
Time: 436.179 sec (7 m 16 s)
Start Date: 2024:08:10 08:53:20
End Date: 2024:08:10 09:00:37
Auto launch
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/bin/freshclam --datadir=/usr/local/share/clamav --quiet -l /var/log/clamav/clam-update.log
With execution rights
chmod 755 freshclam
We will now create a log file for updates and make the user clamav owner
touch /var/log/clamav/clam-update.log
chmod 600 /var/log/clamav/clam-update.log
chown clamav:clamav /var/log/clamav/clam-update.log
Another solution for a simple launch as a daemon (launch six times a day) we type
freshclam --datadir=/usr/local/share/clamav -d -c 6 -l /var/log/clamav/clam-update.log
now for an automatic launch of clamd daemon we will create the file clamd.service under /usr/lib/systemd/system, here is its content
[Unit]
Description = clamd scanner
daemon
After = syslog.target
nss-lookup.target network.target
[Service]
Type = simple
ExecStart =
/usr/local/sbin/clamd -c /usr/local/etc/clamd.conf
Restart = on-failure
PrivateTmp = true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
now for the service to
be launched at each boot of the machine you will have to
type
systemctl enable
clamd.service
here is the result
Created symlink from
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/clamd.service
to /usr/lib/systemd/system/clamd.service.
to launch it now just
type
systemctl start
clamd.service
and this is what it gives when you type systemctl status clamd
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/clamd.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2024-08-10 08:52:49 CEST; 8min ago
Main PID: 97655 (clamd)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 9239)
Memory: 1.2G
CPU: 21.897s
CGroup: /system.slice/clamd.service
└─97655 /usr/local/sbin/clamd -c /etc/clamd.conf
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: Mail files support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: Mail: RFC1341 handling enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: OLE2 support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: PDF support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: SWF support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: HTML support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: XMLDOCS support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: HWP3 support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: OneNote support enabled.
Aug 10 08:53:11 ultra.kervao.fr clamd[97655]: Self checking every 600 seconds
Automatic scanner launch
For an automatic launch of the scanner you can use cron, create a scanvirus file to place under /etc/cron.daily (every day) or /etc/cron.hourly (every hour) containing
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/bin/clamscan -r -l /var/log/clamscan/scan.log /home
/usr/local/bin/clamscan -r --mbox /var/spool/mail
You must make it executable
chmod 755 /etc/cron.daily/scanvirus. It will scan the /home and /var/spool/mail
directories every day . You are free to add scans in the samba shares or your windows partitions.
Interfacing with sendmail
INPUT_MAIL_FILTER(`clmilter', `S=local:/var/log/clamav/clmilter.sock, F=, T=S:4m;R:4m')dnl
define(`confINPUT_MAIL_FILTERS', `clmilter')
In the event that SpamAssassin is already interfaced with sendmail , you will need to modify the last lines like this.
INPUT_MAIL_FILTER(`clmilter', `S=local:/var/log/clamav/clmilter.sock, F=, T=S:4m;R:4m')dnl
INPUT_MAIL_FILTER(`spamassassin', `S=local:/var/run/spamass.sock, F=, T=C:15m;S:4m;R:4m;E:10m')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_CONNECT',`t, b, j, _, {daemon_name}, {if_name}, {if_addr}')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_HELO',`s, {tls_version}, {cipher}, {cipher_bits}, {cert_subject}, {cert_issuer}')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_ENVFROM',`i, {auth_authen}, {auth_type}')dnl
define(`confMILTER_MACROS_ENVRCPT',`r, v, Z')dnl
define(`confINPUT_MAIL_FILTERS', `clmilter,spamassassin')
In the file /etc/clamd.conf we will modify the following line
# Path to the local socket. The daemon doesn't change the mode of the
# created file (portability reasons). You may want to create it in a directory
# which is only accessible for a user running daemon.
# I didn't set the default directory because the clamav user
# can't write under /var/run
LocalSocket /var/log/clamav/clamd.sock
Now we restart clamd
systemctl restart clamd.service
And we launch clamav-milter
clamav-milter -c /usr/local/etc/clamav-milter.conf
For information even when running it as root, it will be the clamav user who will be the owner of the clamav-milter process . Now we restart sendmail assuming that your conf file is located under /usr/share/sendmail-cf/cf and is named config.mc
systemctl stop sendmail
cd /usr/share/sendmail-cf/cf/
m4 config.mc > /etc/mail/sendmail.cf
systemctl start sendmail
Now to launch clamav-milter automatically, we will create the file clamav-milter.service in the directory /usr/lib/systemd/system/
[Unit]
Description='ClamAV Milter'
After=clamd.service
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/usr/local/sbin/clamav-milter --config-file /usr/local/etc/clamav-milter.conf
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Now for the service to be launched at each boot of the machine you will have to type
systemctl enable
clamav-milter.service
this is the result
Created symlink from
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/clamav-milter.service
to /usr/lib/systemd/system/clamav-milter.service.
to launch it now just
type
systemctl start
clamav-milter.service
and this is what the systemctl status clamav-milter.service command gives
●
clamav-milter.service - 'ClamAV Milter'
Loaded: loaded
(/usr/lib/systemd/system/clamav-milter.service;
enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running)
since Sat 2021-09-11 20:34:04 CEST; 6s ago
Process: 292092
ExecStart=/usr/local/sbin/clamav-milter --config-file
/usr/local/etc/clamav-milter.conf (code=exited,
status=0/SUCCESS)
Main
PID: 292093 (clamav-milter)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4677)
Memory: 2.6M
CPU: 10ms
CGroup:
/system.slice/clamav-milter.service
└─292093 /usr/local/sbin/clamav-milter --config-file
/usr/local/etc/clamav-milter.conf
Sep 11 20:34:04
mana.kervao.fr systemd[1]: Starting 'ClamAV Milter'...
Sep 11 20:34:04
mana.kervao.fr systemd[1]: Started 'ClamAV Milter'.
/usr/local/sbin/clamav-milter: --max-children must be given if --external is not given
Make sure you have uncommented the following line in the /usr/local/etc/clamd.conf file
# Maximal number of threads running at the same time.
# Default: 10 MaxThreads 20
Now how do you know if a virus has been intercepted? With fetchmail when you retrieve the mail you have a message like this
fetchmail:
reading message
olivier.hoarau@funix.org@pop.pro.proxad.net:36 of 37
(3143 bytes) fetchmail: discarded
fetchmail: SMTP server
refused to deliver mail
To have the email
purely and simply deleted. In your .fetchmailrc file you will need
to add the following line
poll
pop.fai.net protocol pop3
user
olivier.hoarau@funix.org with password machinchose
is olivier here
options
antispam 550 554;
Otherwise it will remain in /var/spool/mail . In more detail with journalctl we obtain
Sep 29 17:40:37
ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[658550]: 38TFebXF658550:
from=<adriana@spartoo.com>, size=44494, class=0,
nrcpts=1,
msgid=<0.0.3DE.F.1D9F2E9F7CCA362.0@email.spartoo.com>,
bodytype=8BITMIME, proto=ESMTP, daemon=MTA,
relay=localhost [127.0.0.1]
Sep 29 17:40:37
ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[658550]: 38TFebXF658550:
Milter (clmilter) add: header: X-Virus-Scanned:
clamav-milter 0.105.1 at ultra.kervao.fr
Sep 29 17:40:37
ultra.kervao.fr sendmail[658550]: 38TFebXF658550:
Milter (clmilter) add: header: X-Virus-Status: Clean
X-Virus-Scanned:
clamav-milter 1.2.0 at ultra.kervao.fr
X-Virus-Status: Clean
| [ Back to FUNIX home page ] |
 Welcome
Welcome Linux
Linux Unix
Unix Download
Download